TRULY LOYAL CUSTOMERS
Research Process
Discover, Learn, Test, Measure

Balancing desirability, feasibility and viability, frameworks is a design thinking approach used to test out hypotheses to see if a product contains the elements needed to be successful.
Research makes the design better. The aim is to create products and services that people want to use, by increasing user satisfaction (2) and loyalty (3).
Designing Viable & Desirable Products is Strategic.
Design thinking combines three criteria:
- what is desirable from a customer (a product that users need or want)
- what is economically viable (a product that will be profitable)
- what is technologically feasible (a product that is created with innovative technology)
1. Desirability
To ensure the desirability of your product, it has to solve a problem for customers in a way that’s intuitive and pleasing. It’s not enough that the technology exists and that profits or business benefits may be derived, users need to feel a sense of desirability towards a solution.
There are four UX levels of a product:
- Utility
- Usability
- Desirability
- Brand experience
Usability is the next quality to follow utility. For a product to be usable, it has to be easy to use and intuitive. Desirability is a UX design factor that gives a product that special touch, setting it apart in a market full of similar products in terms of utility and usability.
2. Viability
Designers must consider how the product will impact the business, and what the commercial value of releasing a product. For UX designers, value cannot be a secondary responsibility to usability, it should be a designer's primary focus.
At the same time, UX Designers should own “value to users” (usability).
Product Managers should own “value to customers and the business” (viability).
Walk a Mile in the User’s Shoes and Enhance Their Satisfaction.
UX-centric products perform better. Building empathy for the users is crucial to business success. UX is an ever-changing design field that expands to meet the needs of customers.

1. Basic rules of usability
- Watch and observe what people actually do, while performing tasks with the user interface
- Don't take for granted what people say they do, designers have to discover what users need
- Definitely don't take for granted what people predict they might do in the future, we need to validate assumptions
From a broader perspective, UX Research & Design is a "Business meets Market" process rather than a design technique. It involves continuous product improvement through an iterative design process using testing and measuring the assumptions with real users: UX Research and Market Research. While design principles like usability or adaptability serve as tools for these improvements, UX Design is the methodology that enables the designers to apply and measure these changes systematically. However, customer satisfaction should be the heart of marketing, and UX design should to support it.
Adding qualitative context to quantitative data allows teams to make informed decisions and continuous improvements that align with users' needs and expectations. By tracking and analyzing UX metrics, teams can ultimately create a more user-centric, efficient, and satisfying product.
Work process - Every initial discovery stage starts with kick-off discussions with stakeholders to understand the users, product strategy and business vision. Regular catch-up meetings about discovery follow every design sprint on day 1 or 2.

2. Simplicity (Market) and Findability (UX) always win!

The paradox is that while customers are attracted to products with many options and features, they ultimately prefer using products with fewer options because it makes selection easier. Too many choices can lead to mental exhaustion, making people feel frustrated with the experience or, even worse, abandon the process entirely.
In designing any user interface, key decisions must be made regarding the balance between feature richness and simplicity. Limiting the number of options helps people make decisions more easily and complete tasks more quickly.
One of the biggest causes of user failure is when users simply can’t locate certain things on the application. We have to make it easy for them to locate a feature or piece of content that they know is available (findability) or to find it on their own, without knowing in advance that it exists (discoverability).
Effectiveness
- Task success
- Task completion
Efficiency
- Time on task
- Steps to complete a task
Susceptibility to errors
- Number of error
- Severity of errors
Satisfaction
- Rating scale for enjoyment, usefulness
- Expressions of satisfaction/frustration
Discoverability/Findability
- First clicks
- First impressions
- Expressions of satisfaction/confusion
Learnability
- Time on tasks for repeated tasks
- Task success for repeated tasks
- Number of errors for repeated tasks
- Expressions of mastery/confusion
Customer Loyalty for SaaS Excellence
Customers’ needs should be at the forefront of the business. This will not only drive more sales, but also build customer loyalty in the far future. It measures the emotional bond between the brand and its customer, it's what makes a customer consistently do business with a particular brand, and it derives from customer satisfaction.
Customer satisfaction alone cannot achieve the objective of creating a loyal customer base, therefore, organisations need to find out how to keep their customers, even if they appear satisfied.
Customers are willing to invest their loyalty in business that can deliver superior value relative to competitors. This is why studying competitors is important during the market discovery phase.
Effective strategies to improve customer loyalty and retention
- Create a personalized onboarding process to activate new users.
- Replace long product tours with interactive walkthroughs.
- Offer self-service support to improve customer satisfaction.
- Retain existing customers with secondary onboarding.
- Unlock consistent value for your customer base with webinars.
- Gather customer feedback and act on it to improve customer experience.
- Track the behaviour of loyal customers and replicate their paths.
- Identify drop-off points with funnel analysis and fix them.
- Send re-engagement emails to increase customer retention.
- Implement loyalty programs to strengthen customer relationships.

Different types of loyal customers
Loyal customers tend to be patient when technical issues occur, don’t go about searching for alternative solutions and can easily provide feedback if we ask.
- Happy customers
- Price-loyal customers
- Loyalty program and freebies loyal
- Convenience-loyal customers
- Truly loyal customers
Customer loyalty metrics
- Net promoter score
- Customer Loyalty Index
- Customer lifetime value
Customer retention metrics
- Customer retention rate
- Customer churn rate
- Revenue growth rate
North Star Metric, the core value that the product delivers to customers
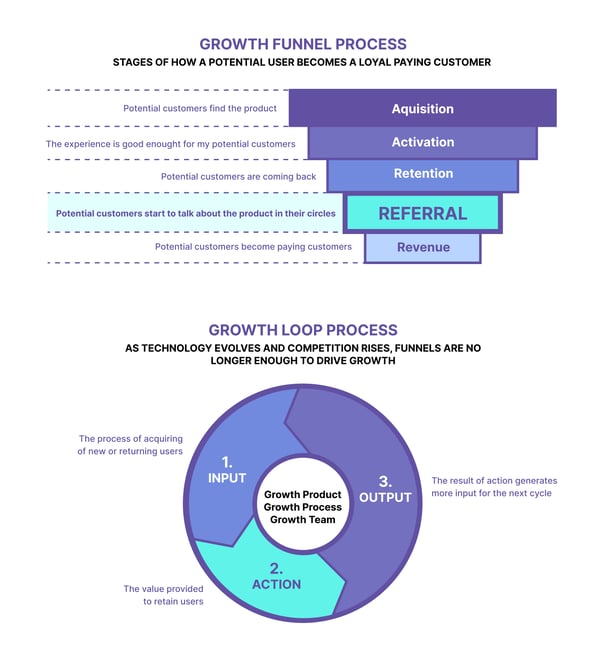
The North Star Metric is for reaching the company's maximum growth potential and developing a simplified long-term growth strategy. The North Star Framework is a strategic approach used by product development teams to align their efforts with business goals and customer-centric outcomes.
It evolves as the company’s strategies, products, and market conditions change over time. For example: Facebook initially focused on monthly active users as its NSM, but later shifted to daily active users to align better with user engagement.
The focus for this metric shouldn't be the revenue. Revenue is the price that the customers pay, while the North Star Metric is the value that the customers get back for that price.
On the other hand, there is another metric with almost the same importance: One Metric That Matters is a one-team focus to achieve rapid growth for a period of 2 to 6 months. The One Metric That Matters is considered a sub-focus of the North Star Metric.To uncover the North Star Metric, we have to understand the value most loyal customers obtain from using the product and quantify it in a single metric. And this is not just a marketing responsibility.
Coordinating sales, marketing, customer support and product teams to work together on growth initiatives can be extremely challenging without a metric of a common goal. For example: Uber - uses the number of trips, Airbnb - the number of nights booked, Spotify - the time spent listening and Facebook - the monthly active users. As for the Proptech industry - how quickly the estate agents sell properties, which directly impacts their revenue and efficiency.
Examples of variables that work together to move this customer metric: are parts of the customer lifecycle such as new user signups, new user activations, and improving engagement and retention of users. SaaS companies usually choose “user adoption rate” or "customer lifetime value" as their North Star Metric, focusing on getting more users to actively use their software.
Market Research in Agile is a Challenge
Collaboration between different team members at each stage of the product workflow is essential. When the product designer seeks to validate product ideas, both the marketing and technical departments should be involved in the process. It’s important to consider what research other teams have done before initiating a new product research process, so as not to waste time duplicating generic market research.
Both UX research and market research methods aim to provide insights into consumer behaviour, but they differ in their focus, timing and methodology.
Focus
- UX Research focuses on understanding the user experience of a product. It aims to identify user needs, pain points, and behaviours to improve the design and functionality of a product.
- Market Research focuses on the audience target (how the customers react to a product, their opinions and feedback), the market and product competition.
Methodology
- UX Research typically leans more heavily on qualitative methods such as user interviews, usability testing, and surveys. These methods provide in-depth insights into user behaviour and attitudes.
- Market Research often uses quantitative methods such as surveys, analytics, A/B testing. These methods provide statistical insights into market trends and consumer behaviour.
Timing
- UX Research is conducted during the product development process, allowing designers to iterate and improve the product based on user feedback.
- Market Research is conducted before product development begins. It informs business decisions such as product positioning, pricing, and marketing strategy.
To create successful user-centric products, the goal is to conduct some research every sprint and then make room to continually learn and refine the product or feature objectives with each iteration. Research and Design should be equally important.
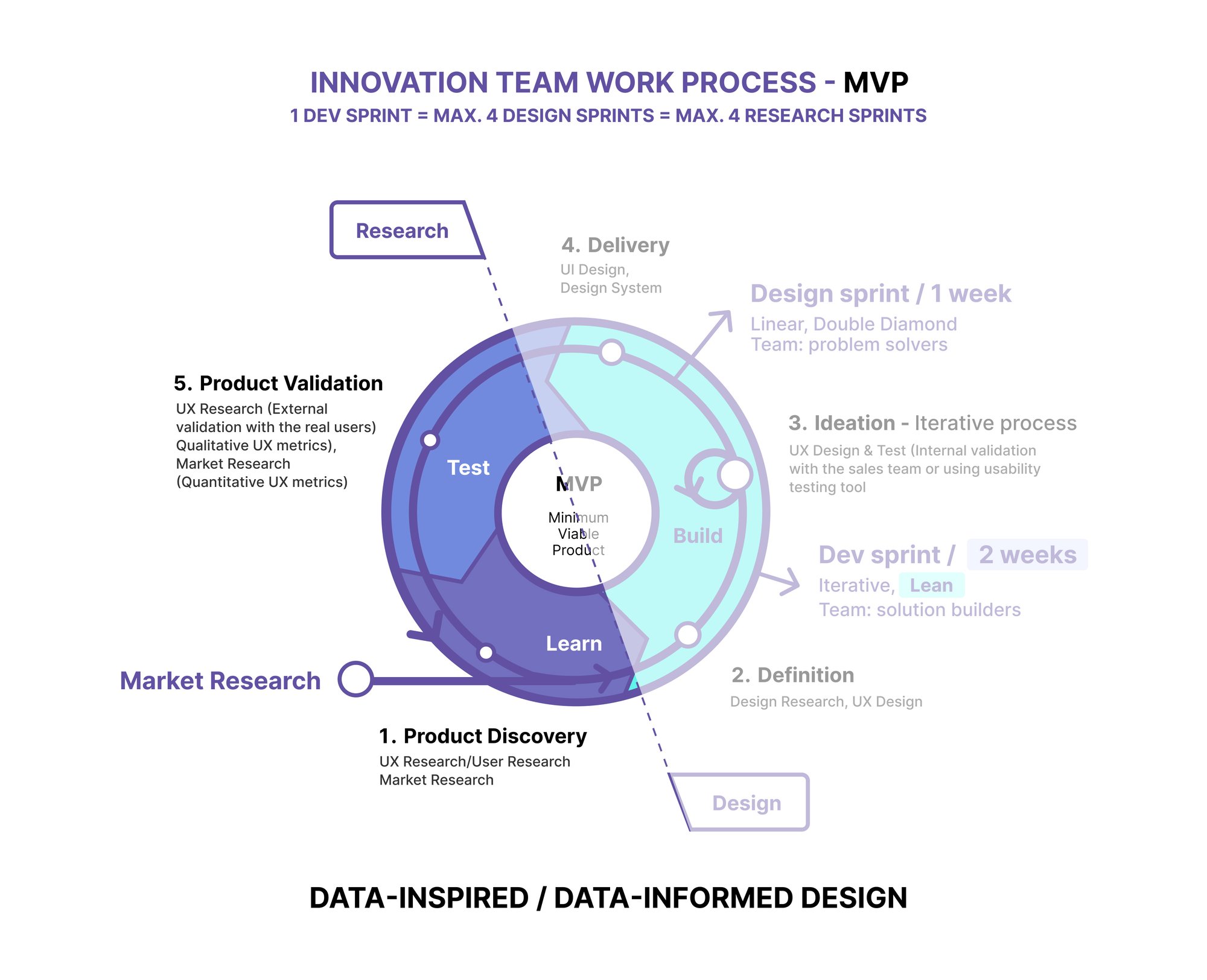
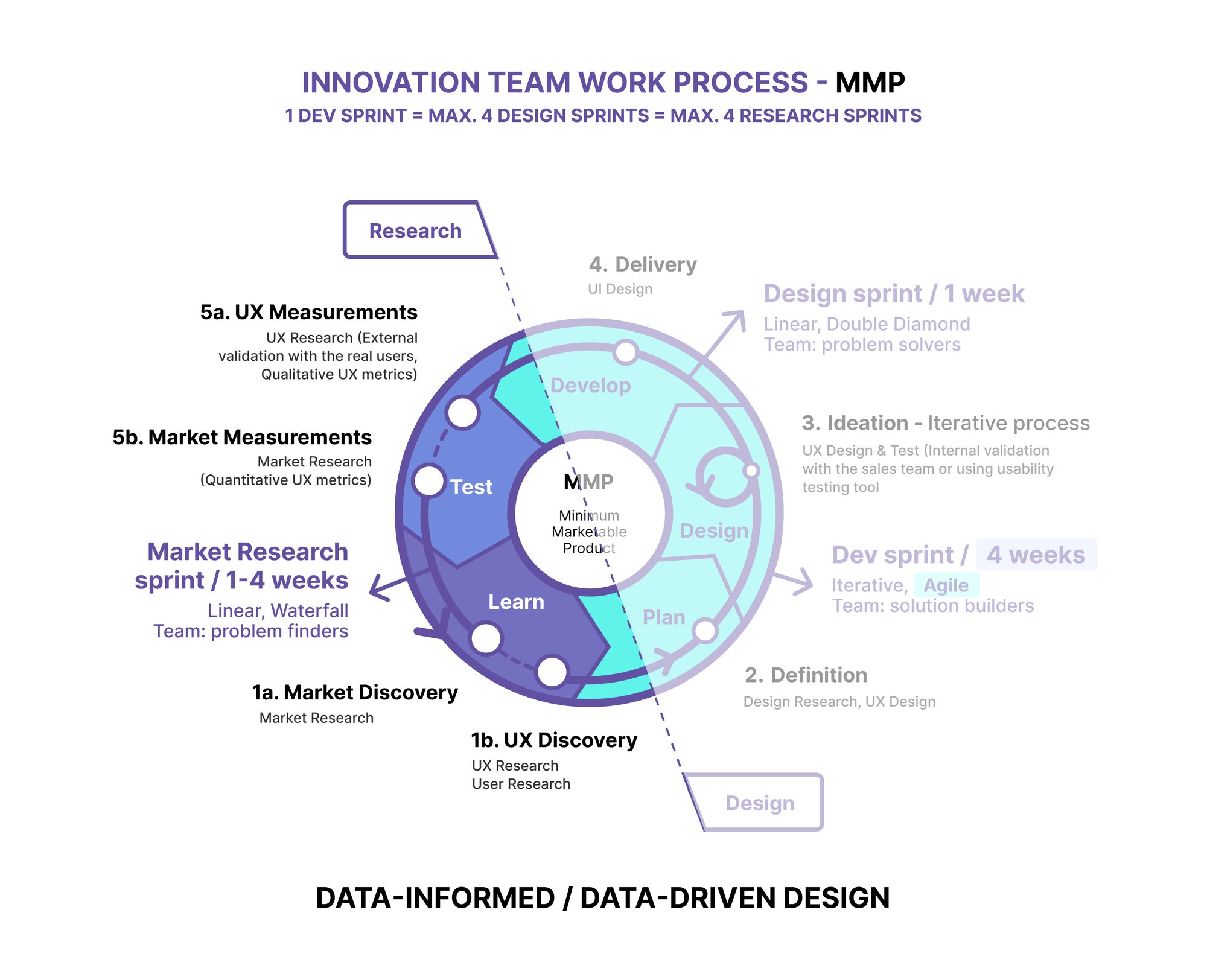
To document research on the backlog, the research team follows a few steps:
- Divide the study into bite-sized pieces and add corresponding tasks within the research backlog item
- Once all the tasks are completed in this backlog item, this research effort is considered done and can be closed out
- Upon completing the research, the research team will likely have a list that includes bug fixes, UX debt, potential new features, and opportunities for further research.
Learnings from the research will inform the team about users' needs and upcoming.
Research Templates
Usability tests, User interviews, Gap analysis and many more
This webpage is currently under construction. Please disregard the content below for now.
Clarification
Why customer-centric teams prefer a data-informed design process?
"Data-driven" involves teams guided by data. But being data-driven doesn’t always lead the team down the path that’s best for the business' customers.
Data-driven means making decisions based solely on data. Data-informed means using data as one of several inputs, alongside factors like your company’s objectives and employee expertise, in decision-making.
![]()
Customer-centric product teams need to combine quantitative, numerical data with qualitative data analysis to reveal real user behaviour and needs. Some of the best ways to get deeper insights and make data-informed product decisions include heatmaps, recordings, surveys & feedback, user interviews.
More data isn’t always better. The product team can have all the data in the world, but if it’s not accurate or doesn’t address the right questions, it will not help the team to make the decisions that lead to meaningful results. Being data-informed means the team understands which data is the most important, and to prioritize quality data to underpin the business decisions.
How to build a Design Systems at Scale? Can it be considered a digital product itself?
Decades ago, we didn’t know the difference between a visual style guide, component library, design language, or design system.
![]()
A healthy design system will make it easier to scale design patterns and components alongside a growing design/product team. It ensures consistency and quality across all experiences and increases the speed without losing best practices or consistency within the product.
There are a few steps to follow in scaling the design system across different products and platforms:
- align the design system with product vision and goals: purpose, scope, and value of the design system, and how it supports the company's brand identity, user needs, and business objectives.
- establish a governance model that defines the roles, responsibilities, and processes for creating, updating, and using the design system
- modularize and standardize the components, so that they are easy to reuse, customize, and maintain across different products and platforms
- adapt it to different contexts and needs of the products and platforms by considering: the diversity and specificity of the users, devices, environments, and scenarios. How do these factors affect the design decisions and outcomes? The design systems need to be tested and evaluated in different contexts and needs, then collect and analyze feedback.
- promote a culture of collaboration and learning among the design, product, development team and other stakeholders.
- evaluate and measure the impact and value of the design system, and test if it meets the business vision and goals. Identify the gaps and opportunities, and prioritize and implement the necessary changes and enhancements.
Why choose qualitative research over quantitative research?
It depends on what kind of project is going to be handled. Qualitative Research is a method generally used for understanding user's views and perceptions. It offers visions for different problems and helps in developing concepts or theories for potential quantitative research.
![]()
This method uses various kinds of unstructured or semi-structured practices for data collection such as group discussions or individual interviews. It helps in interaction among respondents, as they depend on the comments, perceptions, views, opinions and ideas of people. It involves respondents more than in a structured survey (Quantitative Research). It uses in-depth analysis of small groups of people for building theories. The results of qualitative research are not predictive, but descriptive.
What are design tokens in Figma?
![]()
Design tokens are a method for managing design properties and values across a design system. Each token stores a piece of information, such as colour, sizing, spacing, font, animations, and so on. To make them easier to refer to, each token also gets a name.
The tokens become a source of truth and a shared language between design and code, making updating the designs and design systems more efficient.
Source: Figma Learn


